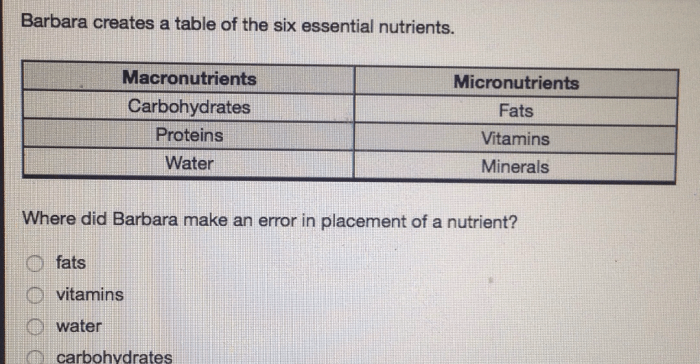
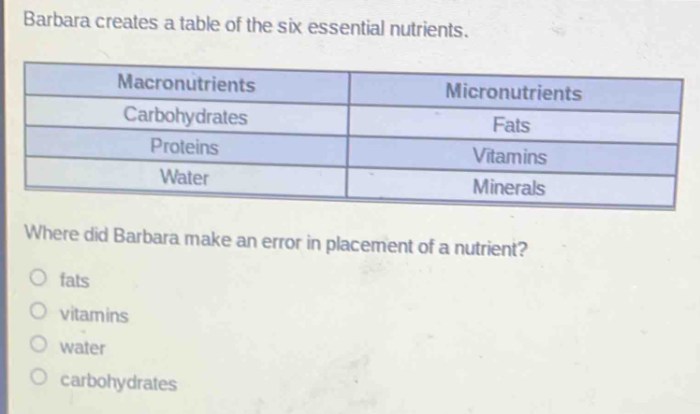
Barbara creates a table of the six essential nutrients – Barbara’s meticulously crafted table of the six essential nutrients provides a comprehensive guide to the fundamental building blocks of human health. Each nutrient plays a critical role in supporting various bodily functions, from energy production to immune defense. By understanding the functions, sources, and recommended daily intake of these essential nutrients, we can optimize our diets and enhance our overall well-being.
Essential nutrients are indispensable for maintaining optimal health. They cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained from our diet. The six essential nutrients highlighted in Barbara’s table are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. Each nutrient has unique functions and contributes to specific physiological processes.
Overview of Essential Nutrients
Essential nutrients are substances that the body cannot produce on its own and must be obtained from food. They play crucial roles in various bodily functions, including energy production, growth and development, tissue repair, and immune function.
Essential nutrients can be classified into two main categories: macronutrients and micronutrients. Macronutrients are required in large amounts and include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Micronutrients, on the other hand, are required in smaller amounts and include vitamins and minerals.
Barbara’s Table of Essential Nutrients
| Nutrient | Functions | Sources | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | – Primary source of energy for the body
|
– Grains (e.g., bread, pasta, rice)
|
45-65% of total calories |
| Proteins | – Building blocks of tissues
|
– Lean meats
|
10-35% of total calories |
| Fats | – Provide energy
|
– Healthy oils (e.g., olive oil, canola oil)
|
20-35% of total calories |
| Vitamins | – Regulate metabolic processes
|
– Fruits
|
Varies depending on the specific vitamin |
| Minerals | – Support bone health
|
– Dairy products
|
Varies depending on the specific mineral |
| Water | – Regulates body temperature
|
– Drinking water
|
Approximately 8 cups per day |
Functions and Sources of Essential Nutrients
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which is used by cells for fuel. Carbohydrates also help regulate blood sugar levels and provide fiber, which is important for digestive health.
Proteins
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues. They are also involved in enzyme production and hormone regulation. Proteins can be obtained from both animal and plant sources.
Fats
Fats provide energy and insulation. They are also involved in hormone production and cell signaling. Healthy fats can be found in foods such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
Vitamins
Vitamins are essential for a variety of bodily functions, including metabolism, immune function, and growth and development. Vitamins can be divided into two categories: water-soluble vitamins (e.g., vitamin C, vitamin B12) and fat-soluble vitamins (e.g., vitamin A, vitamin D).
Minerals
Minerals are essential for bone health, fluid balance, and muscle function. Minerals can be divided into two categories: major minerals (e.g., calcium, potassium, sodium) and trace minerals (e.g., iron, zinc, iodine).
Water, Barbara creates a table of the six essential nutrients
Water is essential for life. It regulates body temperature, transports nutrients and oxygen, and lubricates joints. Water can be obtained from drinking water, as well as from foods with high water content, such as fruits and vegetables.
Recommended Daily Intake: Barbara Creates A Table Of The Six Essential Nutrients
The recommended daily intake (RDI) of essential nutrients varies depending on age, gender, and activity level. The RDI for each nutrient is determined by the amount that is needed to maintain optimal health.
The RDI for some essential nutrients is as follows:
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% of total calories
- Proteins: 10-35% of total calories
- Fats: 20-35% of total calories
- Calcium: 1,000 mg per day for adults
- Iron: 18 mg per day for adult women, 8 mg per day for adult men
- Vitamin C: 65-90 mg per day
Benefits of Consuming Essential Nutrients
Consuming adequate amounts of essential nutrients has numerous health benefits. Essential nutrients help to:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes
- Boost the immune system
- Improve cognitive function
- Increase energy levels
Consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods is essential for good health and well-being.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the six essential nutrients?
Barbara’s table includes carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water as the six essential nutrients.
Why are essential nutrients important?
Essential nutrients are vital for maintaining optimal health as they support various bodily functions and cannot be synthesized by the body.
How can I ensure I consume enough essential nutrients?
By following Barbara’s table and incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, you can meet your daily nutrient requirements.