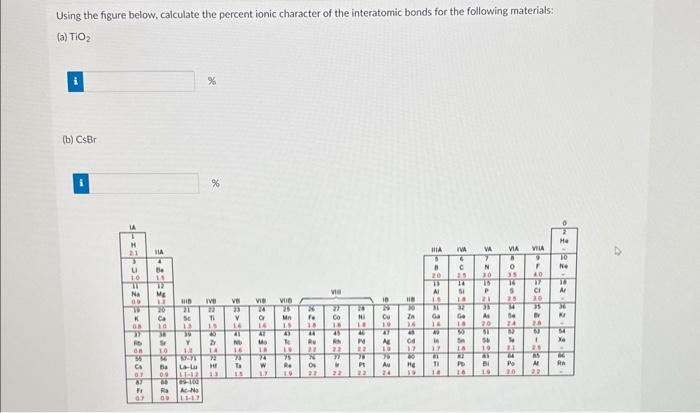
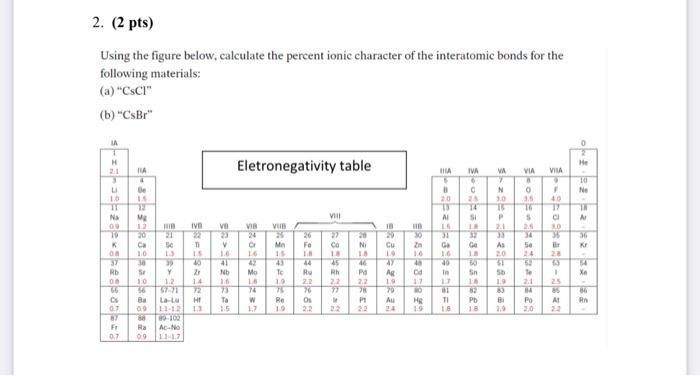
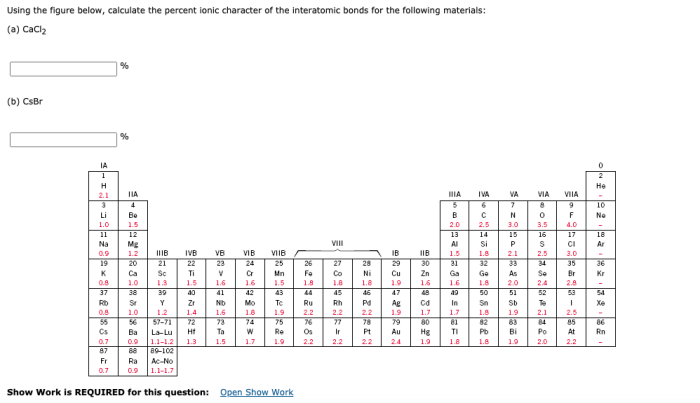
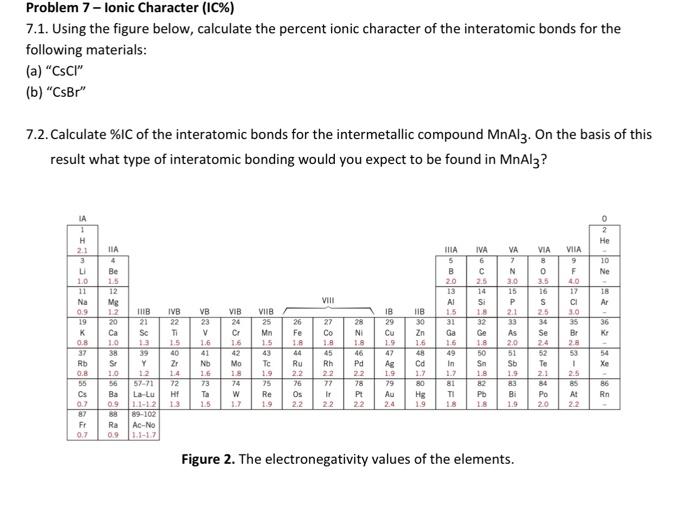
In the realm of chemical bonding, quantifying the ionic character of interatomic bonds holds paramount importance. This endeavor, known as “compute the percent ionic character of the interatomic bonds,” unravels the intricate interplay between electronegativity, atomic radii, and the resulting polarity of chemical bonds.
By delving into the depths of this concept, we embark on a journey to elucidate the factors that govern ionic character, unveil the methods employed to calculate it, and explore its profound implications in predicting the physical and chemical properties of compounds.
Understanding the Concept of Ionic Character
Ionic character refers to the degree of ionic bonding in a chemical compound. It represents the extent to which the atoms in a compound exhibit ionic properties, such as the formation of charged ions and electrostatic attraction between them. Understanding ionic character is crucial for comprehending the nature of chemical bonding and predicting the physical and chemical properties of compounds.
Factors that influence ionic character include the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms and their atomic radii. Electronegativity measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself, and a large electronegativity difference between two atoms leads to a greater tendency for ionic bonding.
Additionally, smaller atomic radii facilitate closer approach of the atoms, enhancing the electrostatic attraction and increasing ionic character.
Examples of compounds with varying degrees of ionic character include sodium chloride (NaCl), which exhibits a high degree of ionic character due to the large electronegativity difference between sodium and chlorine, and hydrogen chloride (HCl), which has a covalent character due to the relatively small electronegativity difference between hydrogen and chlorine.
Methods for Calculating Percent Ionic Character
Several methods exist for calculating the percent ionic character of a chemical bond. One common approach is the Pauling method, which uses the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms to estimate the ionic character. The Born-Haber cycle method, on the other hand, utilizes thermodynamic data to determine the ionic character of a compound.
Other methods include the Phillips method, which considers the ionization energy and electron affinity of the atoms, and the Van Arkel method, which relies on the lattice energy and hydration enthalpy of the compound. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific compound and the available data.
Applications of Percent Ionic Character: Compute The Percent Ionic Character Of The Interatomic Bonds
Percent ionic character plays a significant role in predicting the physical and chemical properties of compounds. Compounds with a higher ionic character tend to have higher melting points, lower solubility in nonpolar solvents, and greater electrical conductivity. This is because the strong electrostatic attraction between the ions in these compounds requires more energy to overcome.
For example, sodium chloride, with its high ionic character, has a high melting point and is soluble in polar solvents but not in nonpolar solvents. In contrast, hydrogen chloride, with its covalent character, has a low melting point and is soluble in both polar and nonpolar solvents.
Advanced Considerations
The concept of ionic character can be extended to include partial ionic character, where the bonding between atoms exhibits both ionic and covalent characteristics. Determining the exact percentage of ionic character can be challenging, and there are ongoing developments in the field of ionic character analysis.
Recent research has focused on developing more accurate methods for calculating ionic character and exploring the relationship between ionic character and other properties of compounds. These advancements contribute to a deeper understanding of chemical bonding and the behavior of chemical compounds.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of ionic character in chemical bonding?
Ionic character provides a quantitative measure of the polarity of a chemical bond, indicating the extent to which electrons are transferred between atoms.
How does electronegativity difference influence ionic character?
The greater the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, the more ionic the bond becomes.
What is the Pauling method for calculating percent ionic character?
The Pauling method utilizes electronegativity values to calculate percent ionic character based on the following formula: % ionic character = 100 – (1 – e^(-0.25 – (χA – χB)^2)), where χA and χB represent the electronegativities of atoms A and B, respectively.