Anatomy of the Respiratory System Review Sheet delves into the intricate network of structures that facilitate the vital process of respiration. This comprehensive guide unveils the complexities of the respiratory system, providing a thorough understanding of its anatomy, functions, and clinical significance.
From the nasal cavity to the alveoli, the respiratory system is a remarkable symphony of interconnected components, each playing a crucial role in gas exchange and maintaining homeostasis. This review sheet serves as an indispensable resource for students, healthcare professionals, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of this fascinating system.
1. Overview of the Respiratory System

The respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the external environment. It consists of two main divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.
The diaphragm, a large muscle located at the base of the thoracic cavity, plays a crucial role in respiration by contracting and relaxing to alter the volume of the chest cavity.
2. Upper Respiratory Tract
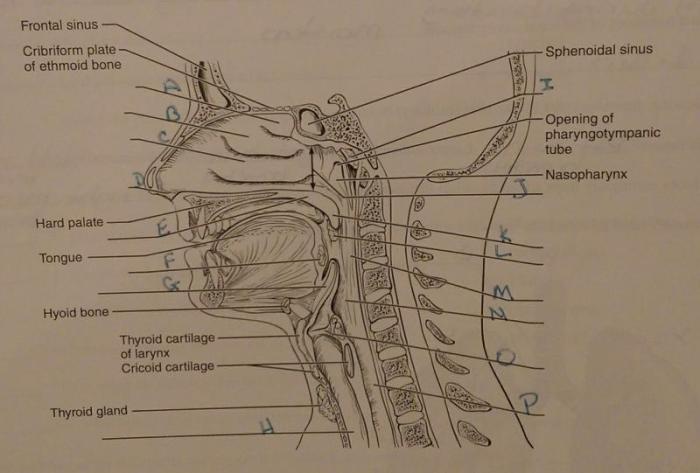
Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity is lined with mucous membrane and contains turbinates, which are bony projections that increase the surface area for air filtration and warming.
Pharynx
The pharynx is a muscular tube that serves as a passageway for air and food. It is divided into three regions: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
Larynx
The larynx, also known as the voice box, contains the vocal cords and is responsible for phonation (producing sound).
3. Lower Respiratory Tract: Anatomy Of The Respiratory System Review Sheet

Trachea
The trachea is a tube-like structure that connects the larynx to the bronchi. It is lined with ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium and contains cartilage rings for support.
Bronchi
The bronchi are the two main branches of the trachea that enter the lungs. They continue to branch into smaller bronchioles, which eventually lead to the alveoli.
Alveoli
Alveoli are small, sac-like structures where gas exchange occurs. They are lined with a thin layer of squamous epithelium and surrounded by capillaries.
4. Respiratory Muscles

Primary Muscles of Inspiration
- Diaphragm
- External intercostal muscles
Role of Intercostal Muscles, Anatomy of the respiratory system review sheet
The intercostal muscles are located between the ribs and assist in both inspiration and expiration.
Mechanism of Expiration
Expiration is primarily a passive process driven by the recoil of the lungs and the elastic recoil of the chest wall.
5. Gas Exchange
Diffusion Across Respiratory Membrane
Gas exchange occurs across the respiratory membrane, which is composed of the alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, and the basement membrane.
Factors Affecting Gas Exchange
- Partial pressure gradients of gases
- Surface area of the respiratory membrane
- Thickness of the respiratory membrane
Role of Hemoglobin in Oxygen Transport
Hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells, binds to oxygen and transports it to tissues.
6. Respiratory Control
Role of Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata in the brainstem contains the respiratory center, which controls the rate and depth of breathing.
Effects of pH and PaCO2 on Respiration
Changes in blood pH and PaCO2 levels can stimulate or inhibit the respiratory center, adjusting the rate and depth of breathing.
Voluntary Control of Breathing
The cerebral cortex can voluntarily control breathing to some extent, overriding the automatic control by the respiratory center.
7. Applied Anatomy
Clinical Significance of Nasal Polyps
Nasal polyps are non-cancerous growths in the nasal cavity that can obstruct airflow and cause symptoms such as nasal congestion and facial pain.
Pathophysiology of Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways characterized by reversible bronchoconstriction, mucus production, and airway inflammation.
Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is a progressive lung disease that causes airflow limitation and shortness of breath. Management includes bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and lifestyle modifications.
Essential FAQs
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
The primary function of the respiratory system is to facilitate gas exchange, enabling the uptake of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide.
What are the two main divisions of the respiratory system?
The two main divisions of the respiratory system are the upper respiratory tract (nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx) and the lower respiratory tract (trachea, bronchi, alveoli).
What is the role of the diaphragm in respiration?
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities. It plays a crucial role in respiration by contracting and relaxing, causing changes in intrathoracic pressure and facilitating the movement of air into and out of the lungs.